The Transformation of Iranian Livestock Farming: From Traditional to Smart (The Dawn of the Fourth Industrial Revolution in the National Livestock Industry)
- Introduction: From Traditional to Industrial and Smart Farming
Traditional livestock farming was prevalent in Iran until ۱۳۲۰ (۱۹۴۱). Following that, with the introduction of new technical knowledge, Industrial Livestock Farming grew from ۱۳۲۰ (۱۹۴۱) to ۱۴۰۴ (۲۰۲۵).
The Third Industrial Revolution in Iranian livestock farming began in ۱۳۷۹ (۲۰۰۰) with the intensified importance of Data and the emergence of Big Data and statistical analysis. During this period, data-driven concepts penetrated areas such as Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Animal Nutrition, Hoof Trimming, Mastitis, and more.
In ۱۳۹۸ (۲۰۱۹), predicting the future needs of the industry and with Modiran Tahlilgar Sepahan Company shifting its focus towards using the Internet of Things (IoT), the groundwork for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in the country’s livestock industry practically began. This path continued until ۱۴۰۲ (۲۰۲۳) with the participation of universities, creative centers, and technology companies, and in this year, a new type of livestock farming, known as Smart Dairy Farming, was born.
- Goals of Smart Livestock Farming
The goal of Smart Livestock Farming is to reduce costs and increase profitability in farming operations. This is crucial because the industry faces four main threats:
| Row | Threat Factor |
| ۱ | Scarcity of vital resources such as Water |
| ۲ | Scarcity or high cost of Energy Carriers |
| ۳ | Migration of Specialists and changing labor force preferences |
| ۴ | Price increase of products due to rising cost of Raw Materials |
Therefore, the fundamental solution is to Increase Productivity while Reducing Costs, a goal pursued through data analysis, smart decision-making, and data-driven management.
- DHI Science: The Backbone of Smart Livestock Farming
To ensure the correct development path, the DHI (Dairy Herd Improvement) science, which has a history of over ۱۲۰ years, was chosen as the scientific backbone of smart livestock farming in Iran. This science emphasizes that achieving sustainable profit requires using data in all management layers.
Fundamental Principles of DHI:
- Analyzing information for Herd Management.
- Improving and focusing on Information.
- Improving Herd Health.
- Increasing the Economic Lifespan of the animal.
- Improving the status of Milk Production.
- Productivity in Animal Nutrition.
- Improving the Genetic Value of the animal.
- Targeted Culling.
- Increasing Herd Profitability and making the farm economically viable.
- Formation of the Smart Livestock Farming Committee
In ۱۴۰۳ (۲۰۲۴), the Smart Livestock Farming Committee was established as one of the main pillars of the country’s knowledge-based associations. This committee is mandated to:
- Identify Technologists and Startups active in the field of digital livestock farming.
- Support Creative Projects in the field of smart farm automation.
- Strengthen the link between the Industry and Academia in this field.
- Smart Livestock Farming Roadmap
The roadmap for this major transformation is based on Data, IoT, and Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- The speed and accuracy of Data Collection are increased by using IoT Equipment.
- Based on the collected data, Human and Machine Analysis are performed at the herd level.
- Artificial Intelligence analyzes the herd’s information and offers Suggestions for Improving Productivity.
- Reports and real-time Notifications are provided to the farmer in the form of a management Dashboard.
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
The primary KPI for the implementation of smart livestock farming is the degree of participation of Machines and Automated Systems in Data Processing. The national target is to increase the machine’s share from the current ۱% to ۴۰%.
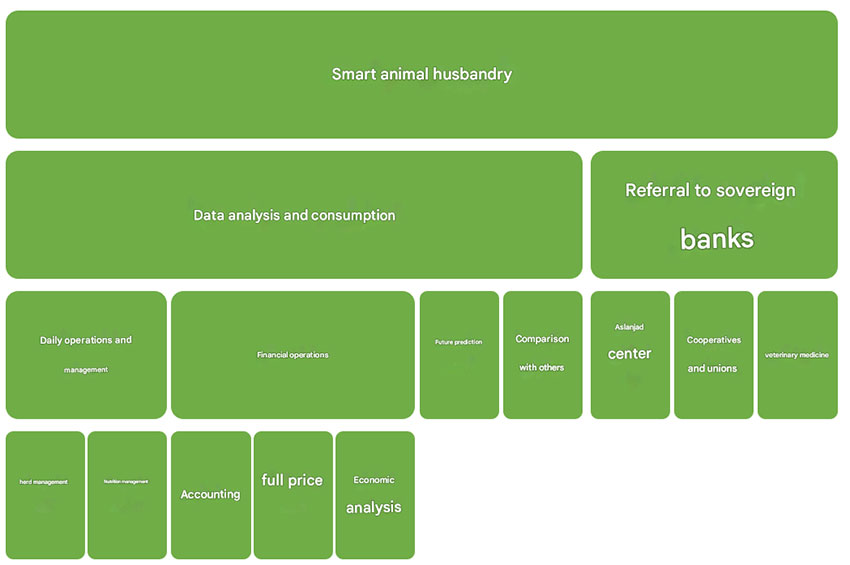
- Structure and Categorization of Smart Livestock Farming
According to the official document “Categorization of Smart Livestock Farming,” the overall structure of this industry is composed of several layers. The main domains and their functions are provided in the table below:
| Main Domain | Sub-Categories | Function |
| Data Analysis and Consumption | Herd Management, Nutrition Management, Financial Operations, Accounting, COGS, Economic Analysis, Future Prediction, Comparison with Others | Analysis of operational and managerial data |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Animals, Locations, Equipment | Identification, measurement, monitoring, and data transmission |
| Servers and Artificial Intelligence | Database Servers, Information Storage, Data Comparison | Advanced analysis and machine learning |
| Daily and Management Operations | Control of daily processes, task allocation, animal health monitoring | Operational coordination and rapid decision-making |
| Nutrition and Feed | Feed Factory, Composition, Formulation, Consumption Monitoring | Quality control and optimization of feed rations |
| Equipment | Fixed and Mobile, Vibration and Sound, PM positioning (Preventive Maintenance) | Accurate measurement and preventive maintenance |
| Locations | Laboratory, Pens, Milking Parlor, Cold Storage, Holding Environment | Collection of environmental data and control of THI (Temperature, Humidity, Ammonia, and CO₂) |
| Consumables | Water, Semen, Embryos, Medication | Measurement of quality and control of resource consumption |
| Communication with Upstream Institutions | Breeding Centers, Cooperatives, Veterinary Services | Data exchange and smart reporting with the national network |
- Conclusion and Future Outlook
The smart transformation of livestock farming is an irreversible path in the evolution of Iran’s livestock industry. By developing IoT infrastructure, data analysis, and AI, it becomes possible to monitor processes, predict production, manage energy, and reduce waste. In the near future, with the full achievement of the defined KPIs, Iranian livestock farming can become a regional model for sustainability, productivity, and a data-driven economy.