A Novel Simulation Software Program (Rayan) for Systematic Dairy
Herd Data Management
M Vakili1, A Molaei2, S Sakian3, H Mousapour4, S Mokhtarzadeh4, MH Khabbazan4 and Akbar Nikkhah4,5*
۱Modiran Analytics Sepahan Co., Isfahan, Iran
۲Dasht-e-Naz Agricultural and Livestock Co., Sari, Mazandaran, Iran
۳Fajr-e-Isfahan Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Co., Isfahan, Iran
۴Ferdows Pars Agricultural and Livestock Holding Co., Tehran, Iran
۵Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Tehran, Iran
*Corresponding Author: Akbar Nikkhah, Ferdows Pars Agricultural and Livestock Holding Co., Tehran, Iran.Received: February 08, 2021Citation: Akbar Nikkhah., et al. “A Novel Simulation Software Program (Rayan) for Systematic Dairy Herd Data Management”. EC Veterinary
Science 6.8 (2021)
Abstract
Modern dairy herds rely greatly on digital and computer-based programs and techniques for precise and accurate data management. The objective of this technical research was to develop and describe a novel simulation software program for management of dairy herd big data. The current simulation program (Rayan) evaluated and utilized 643 management parameters. The simulation software program (Rayan) is capable to reliably and precisely predict herd composition, income over feed cost, heat detection, fertility, and other reproductive indices, as well as animal sale management and milk strategic marketing. Such a capability would ensure that dairy management annual budgets are developed with high precision. In addition, potential management risks may be predicted, tackled, and prevented in coming years. The program enables present and past times management and can be linked to different other major programs of dairy herd management. Moreover, different items prices, total income, and total cost may be accurately calculated. Furthermore, rates of animal purchase and sale can be predicted based on current management conditions and capacities. Management coefficients developed may also be tested and applied to small ruminant herds. Future applications will include optimizing milking and feeding management. Development of this simulator software program is at the frontier of optimizing dairy research and development in strategic and systematic manners.
Keywords: Big Data; Simulation; Software; Dairy Herd; Management; Prediction
Introduction
Modern dairy ruminant management depends highly on digital and computer-based programs [1,2]. Ideally, such programs should be able to utilize the present and past data to predict future events [2,3]. Precision dairy farming has already been introduced as a practical concept to enable precise predictions of cow health, nutrition, reproduction, and their environmental impacts [4,5]. The ability to predict reliably and precisely is of utmost importance [6,7]. For instance, a major goal in any dairy herd is to reduce costs and increase income. This goal may be achieved through increasing milk production and reducing feed and labour costs. There are numerous management factors that influence milk production and feed/labour costs. These factors first need to be identified. Then, their magnitude of significance
.
in affecting income and costs need to be quantified [1,8]. Predicting reproductive efficiency and performance is another main factor that
needs to be included in any herd management modelling program. As another example, the analysis of reproductive performance in lactating
cows on large dairy farms can be conducted using machine learning algorithms [9].
In addition, different costs associated with animal replacement could be evaluated and precisely determined or predicted. Rate, reasons,
parity, and age of culling may be reliably predicted to enable quantifying their contributions to net incomes. Moreover, feeding programs
need to be developed in such ways that would permit prediction of feed ingredients availability and cost as well as health indices.
For instance, over-consumption of concentrates and cereal grains should be avoided [10]. Such guidelines can be defined and demarcated
to be incorporated in new simulation software programs.
The above-mentioned factors and their multidimensional interactions characterize a very complex system that requires a simply-touse-
and-apply simulation program. The simplicity in application of a simulation software program is the only approach to overcome the
main challenge of the above systematic complexity.
Objective of the Study
The main objective of this technical research was to develop a simple-to-use-and-apply simulation software program to store, process,
and predict a variety of important dairy herd management indices and properties.
Methodology and Discussion
First, 643 management parameters (health, reproduction, nutrition, and animal purchase and sale related parameters) were evaluated
and amalgamated to generate the initial form of combined information to be simulated. After data amalgamation, a variety of software
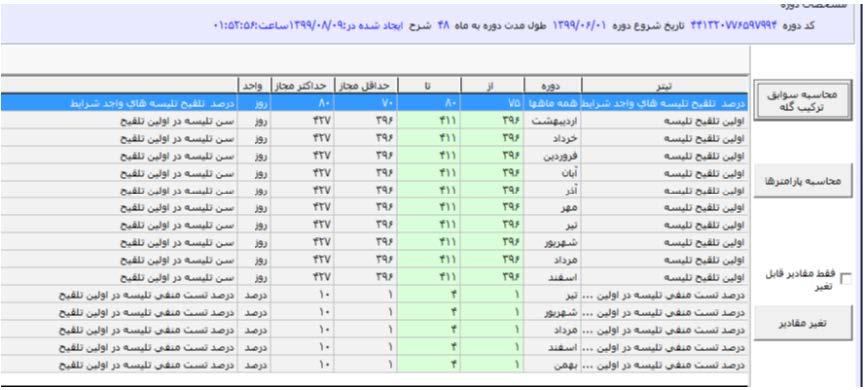
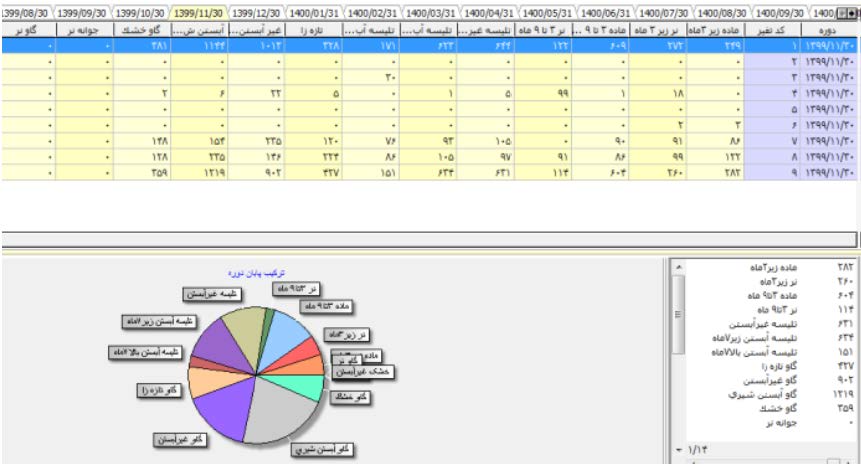
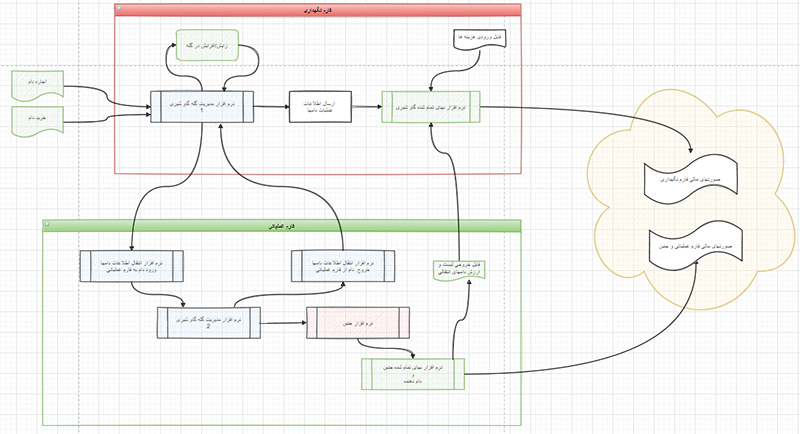
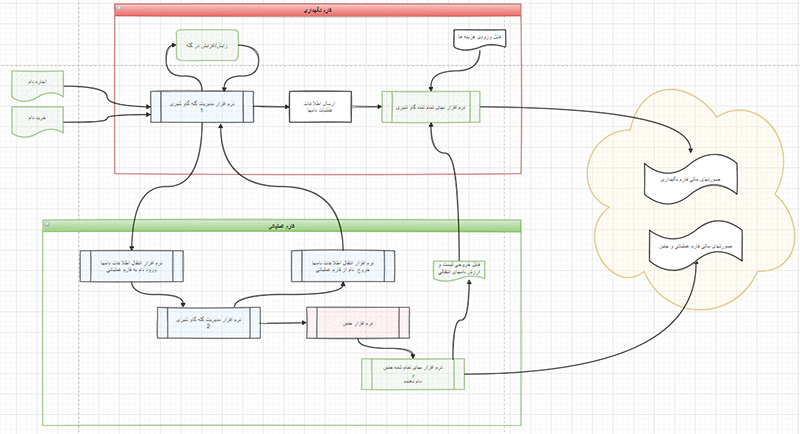
formulations were designed and formulas were extended to enable future predictions (Figure 1-8).
Figure 1: After evaluation and amalgamation of 643 management parameters (health, reproduction, nutrition, animal purchase and sale,
and milk management related parameters), the initial form of information was developed to be simulated.
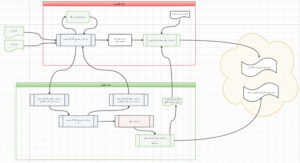
Figure 2: After data amalgamation, a variety of software programs and formulas were designed and formulations were extended to enable
future predictions.
Figure 3: The simulation software program utilizes the current and past data to be able to reliably and precisely predict future events. The
information used includes coefficients, processes, and different factors affecting outcomes. This particular figure illustrates heifers’ insemination
properties and reproduction management and the outcomes.
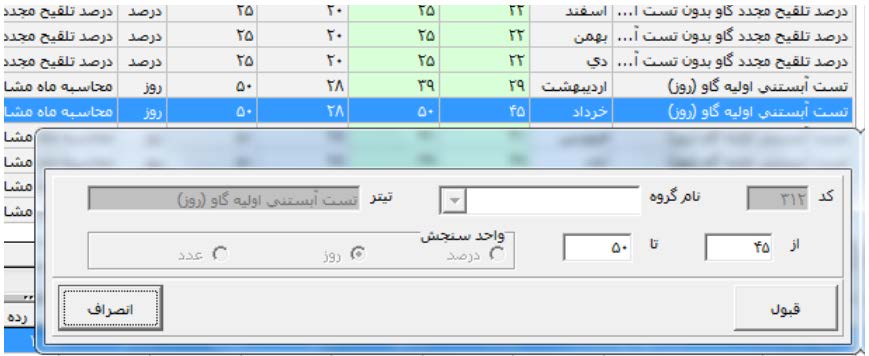
Figure 4: The program enables the user to manipulate and modify management coefficients and predict how it affects herd management.
For example, users can plan to reduce abortion rate and increase female birth (using sexed semen).
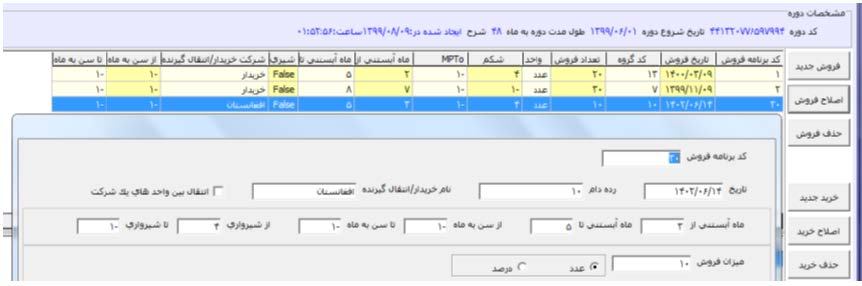
Figure 5: The events that occur during an estimable period of time can be entered and added to the simulation program. These include
animal sales and purchases in different animal categories (e.g., pregnant vs. non-pregnant, heifer vs. cow, dry vs. milking cow).
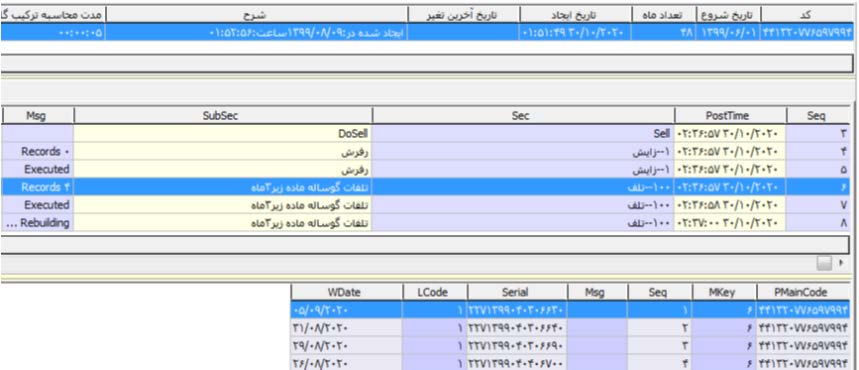
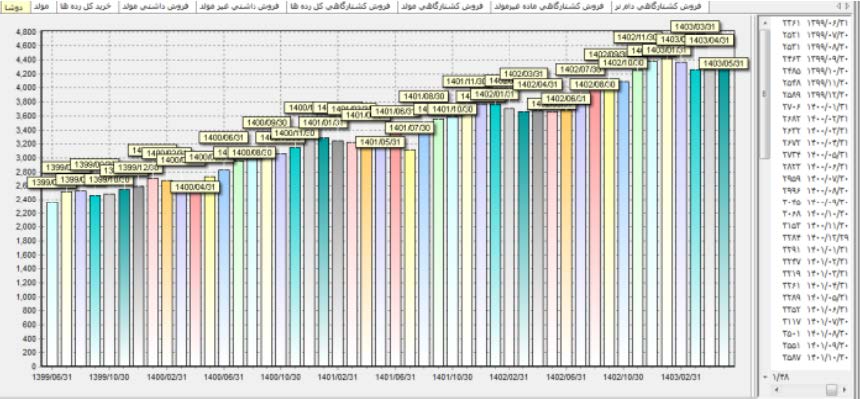
Figure 6: After data acquisition and processing, calculations can be made for upcoming periods of time (e.g., years to come). The simulation
software program is equipped with powerful error-detecting and reporting tools in this regard.
This simulation software program utilizes the current and past data to be able to reliably and precisely predict future events. The
information used includes coefficients, processes, and different factors affecting the outcomes. These particular properties illustrate production
and reproduction management policies and their outcomes. The simulation program enables the user to manipulate and modify
management coefficients and predict how it affects herd management criteria. For example, users can reduce abortion rate and increase
female birth (using sexed semen). The events that occur during an estimable period of time can be entered and added to the simulator
program. These include animal sales and purchases in different animal categories (e.g. pregnant vs. non-pregnant animal, heifer vs. cow,
dry vs. milking cow). After data acquisition and processing, calculations can be made for upcoming periods of time (e.g. years to come). To
Figure 7: After calculations are executed and finished, the outcomes may be illustrated in different forms and in terms of time (e.g. month)
and herd composition and different herd population properties.

note, the simulation software is equipped with powerful error-detecting and reporting tools in this regard. After calculations are executed
and finished, the outcomes may be illustrated in different forms and in terms of time (e.g. month) and herd composition (Figure 1-8).
Figure 1 to 8 illustrate in consecutive order how the simulation software program was developed and how it operates.
Because the simulation program builds its own coefficients after the analysis of herd data, it is capable to state where we have come
from in any aspect. In other words, the program is able to standardize all sub-standard or non-standard values. Moreover, since the Rayan
simulation software has been written with extendable patterns, it has the ability to be linked to other softwares and programs. This means
that by using total feed cost of milk production in nutrition software, the Rayan program can estimate future risk factors in dairy herd
nutritional management. Thus, it will enable modifying and manipulating future feeding and nutritional strategies to optimise dairy herd
productivity and health.
Furthermore, one of the most notable capabilities of Rayan simulation program is risk assessment. This would imply that the simulation
program is able to reduce future risks and accelerate dairy science education and edification [6]. The greater the data within the
simulation program, the greater the ability to evaluate massive management challenges. This analysis would be done without major
financial and time-related costs. For instance, identifying the highest and lowest voluntary waiting period (VWP) cows within 10% limit
could be easily conducted within few hours without any financial needs.
Future goals include milk yield estimation for individual cows at different stages of lactation based on lactation curve properties, development
of precision calculations and economic coefficients for other cow breeds (other than Holstein) and small ruminant herds (e.g.
sheep and goat), and advancement of technology change indices applicable for altering milking, feeding, and reproductive systems and
protocols.
Conclusion
A novel simulation software program (Rayan) was designed and developed to enable modern dairy farmers to predict and quantify the
future of their management systems in different areas. These areas include, but are not limited to, animal and feed/utility purchases and
sales, feeding and nutrition, fertility and reproduction, semen management, milk sale and processing, and milk marketing. This simulation
program possesses the capability to be linked to other major dairy management programs and process shared data. A most notable
capability of Rayan simulation program is risk assessment that would allow farmers to reduce future risks and accelerate dairy science
education and edification. Development of this simulator software program is at the frontier of optimizing dairy research and development
in systematic and strategic manners. The methodical and tactical dairy herd data management will facilitate information handling
and processing towards sustainable and optimized farm economics.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Ferdows Pars Agricultural and Livestock Holding Co., (Tehran, Iran) for supporting our research and development programs.
Bibliography
۱. Hermans K., et al. “Novel approaches to assess the quality of fertility data stored in dairy herd management software”. Journal of Dairy
Science 100.5 (2017): 4078-4089.
۲. Michels M., et al. “Understanding the adoption of smartphone apps in dairy herd management”. Journal of Dairy Science 102.10
(۲۰۱۹): ۹۴۲۲-۹۴۳۴.
۳. National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle: Seventh Revised Edition. Washington, DC (2001).
۴. Berckmans D and Keita A. “Precision livestock farming ‘۱۷ – Papers presented at the 8th European Conference on Precision Livestock
Farming, September, Nantes, France (2017).
۵. Kamphuis C and Steeneveld W. “Precision dairy farming 2016. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen”. The Netherlands
(۲۰۱۶).
۶. Lokhorst C., et al. “Invited review: Big Data in precision dairy farming”. Animal 13.7 (2019): 1519-1528.
۷. Lacroix R., et al. “Effects of data preprocessing on the performance of artificial neural networks for dairy yield prediction and cow
culling classification”. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 40 (1997): 839-846.
۸. Etherington WG., et al. “The dairy herd management system: Application to dairy herd reproductive management as a bureau onfarm
system”. Veterinary Clinics of North America 3.3 (1987): 545-551.
۹. Caraviello DZ., et al. “Analysis of reproductive performance of lactating cows on large dairy farms using machine learning algorithms”.
Journal of Dairy Science 89.12 (2006): 4703-4722.
۱۰. Nikkhah A. “Optimizing starch nutrition for rhythmic dairy cattle: The sustaining economic and environmental challenges of today’s
industry”. The Iranian Journal of Applied Animal Science (2020).
Volume 6 Issue 8 August 2021
©All rights reserved by Akbar Nikkhah., et al.